Birth Control
Sometimes we need birth control to treat a medical condition. Sometimes we need it because we don’t want children yet or at all. Sometimes we need it because we don’t want any more children.
Whatever your reason for using it is, you can find a safe and affordable prescription in Japan.
Select a section from the left or scroll through to read all about birth control in Japan and see the most common products you can expect at your doctor’s office.
Female Contraceptives
Birth Control Pills
1. How do I get birth control and how much does it cost?
In Japan, birth control pills and IUDs are available at most gynecologists’ offices. You will need to make an appointment (or walk-in visit; check with the clinic/hospital to see if an appointment is necessary) with a gynecologist to discuss your options. If you plan on using the pill or an IUD as birth control, neither of them are covered by insurance. The pill is typically between ¥2,000 and ¥3,500 per month. Unlike other countries, however, your doctor will not give you a prescription that you refill on your own at the pharmacy every month. After the first doctor visit, you will receive one month of medication, and you will need to go back for a follow-up before the end of your first pack. After that, you may receive up to 3 months of pills at a time. You always need to go to the clinic for follow-up to receive refills.
IUDs can cost up to ¥50,000 depending on the IUD you choose, your doctor, and your hospital. IUDs, however, can be used for 3 – 10 years, depending on the IUD type, greatly reducing the per-month cost of contraception compared with the pill. If you decide you want an IUD, see your gynecologist for a consultation. After you and your doctor decide which type of IUD is best for you, you will need to make an appointment for insertion. Insertion is a non-surgical procedure that is typically over in less than 15 minutes.
2. What if I need it to control a disease or condition?
If you need the pill or a hormonal IUD for health-related issues (endometriosis, dysmenorrhea, menorrhagia, fibroids, etc.), insurance may cover a portion of the cost. However, you will need exams and diagnosis from a gynecologist, deeming the pill or IUD necessary for control of your condition. A Mirena (hormonal) IUD may be inserted for as little as ¥15,000 yen, depending on your doctor/hospital.
For more options and more knowledgeable doctors, it is recommended you see a gynecologist at a large, reputable hospital for diagnosis and treatment of conditions and diseases of the female reproductive system.
3. What if I need it to control a disease/condition, but I also need it as a contraceptive?
If you have a health issue that requires a birth control pill or hormonal IUD for control, and also want to use it as a contraceptive, you can tell your doctor the reason you want it is for control of your condition (in order to have insurance coverage). The contraceptive effect of the treatment (i.e. pill or IUD) will then be considered a side-effect of your condition/disease treatment. It should be noted, however, that if you become pregnant while using an insurance-covered contraceptive as a condition/disease treatment, you forfeit your right to file a complaint/sue the company for drug/device failure as a contraceptive.
Also, keep in mind that you cannot just say you need it to control a disease or condition in order to receive insurance coverage; you require a diagnosis from a Japanese gynecologist in order to qualify for the coverage.
4. What if my doctor won’t listen/won’t diagnose me, even though I know something is wrong?
Dealing with doctors, especially gynecologists, in Japan can be frustrating at times. There are good doctors and bad doctors in every country, though, so don’t throw in the towel on a bad egg. As a patient, you are entitled to a second, or even third, opinion. See as many doctors as it takes to find the one that fits, and never feel bad for leaving one behind. Your health is important, and you never have to feel like you’re stuck with an arrogant doctor who won’t listen to you. There are tons of excellent doctors in Japan, so don’t give up if you have trouble at first.
5. I don’t want the pill or an IUD. What about Depo, implants, NuvaRing, etc.?
Alternative contraceptives such as Depo-Provera (injection), contraceptive implants, contraceptive patches, and NuvaRing are not available and are not approved by the PMDA (Pharmaceuticals and Medical Devices Authority), the regulatory authority in Japan. Some of these products can sometimes be found on online stores, but the integrity of the product and credibility of these stores is highly questionable at best. These products are prescription only and obtaining them without a prescription is very dangerous and ill-advised. If you want alternative contraception, receive it from your doctor in your home country before coming to Japan.
Birth Control Pills (Oral Contraceptives)
Birth control pills come in two basic types in Japan: monophasic and multiphasic. In a pack of monophasic birth control pills, all pills have the same hormone dose, with the exception of hormone-free reminder pills in 28-packs. In contrast, the pills in a pack of multiphasic birth control have a gradually strengthening hormone dose over the 21-day period (followed by a 7-day period of reminder pills which contain no hormones in 28-packs).
If you are considering switching to a Japanese birth control pill, check the insert on the brand you are currently using to see if the hormones/dosage of the ones available in Japan (listed below) are comparable to what you are on now. If there isn’t one, talk to your Japanese gynecologist about your options for replacing your current pill.
To learn more about birth control pills, how they work, and their safety and effectiveness, visit Planned Parenthood for reliable information at:
The Morning- After Pill (emergency contraception) is available in Japan by prescription only. If you need this pill, go to your gynecologist as soon as you can and ask for it. It is typically between ¥5,000 and ¥15,000.
To learn more about the Morning-After Pill, how it works, and its safety and effectiveness, visit Planned Parenthood for reliable information at: https://www.plannedparenthood.org/learn/morning-after-pill-emergency-contraception
Monophasic Oral Contraceptives





| Marvelon 28 and Favoir 28 (generic of Marvelon) | ||
|---|---|---|
| White pills | Desogestrel | 0.15mg |
| Ethinyl estradiol | 0.03mg | |
| Green pills | Placebo/reminder pills | |

| Yaz | ||
|---|---|---|
| Light pink pills | Drospirenone | 3 mg |
| Ethinyl estradiol | 0.020 mg | |
| White pills | Placebo/reminder pills | |
Multiphasic Oral Contraceptives

| Ange 21 | ||
|---|---|---|
| Reddish brown pills | Levonorgestrel | 0.050 mg |
| Ethinyl estradiol | 0.030 mg | |
| White pills | Levonorgestrel | 0.075 mg |
| Ethinyl estradiol | 0.040 mg | |
| Yellow pills | Levonorgestrel | 0.125 mg |
| Ethinyl estradiol | 0.030 mg | |

| Ange 28 | ||
|---|---|---|
| Reddish brown pills | Levonorgestrel | 0.050 mg |
| Ethinyl estradiol | 0.030 mg | |
| White pills | Levonorgestrel | 0.075 mg |
| Ethinyl estradiol | 0.040 mg | |
| Yellow pills | Levonorgestrel | 0.125 mg |
| Ethinyl estradiol | 0.030 mg | |
| Red pills | Placebo/reminder pills | |

| Labellefille 21 | ||
|---|---|---|
| Reddish brown pills | Levonorgestrel | 0.050 mg |
| Ethinyl estradiol | 0.030 mg | |
| White pills | Levonorgestrel | 0.075 mg |
| Ethinyl estradiol | 0.040 mg | |
| Light yellow pills | Levonorgestrel | 0.125 mg |
| Ethinyl estradiol | 0.030 mg | |

| Labellefille 28 | ||
|---|---|---|
| Reddish brown pills | Levonorgestrel | 0.050 mg |
| Ethinyl estradiol | 0.030 mg | |
| White pills | Levonorgestrel | 0.075 mg |
| Ethinyl estradiol | 0.040 mg | |
| Light yellow pills | Levonorgestrel | 0.125 mg |
| Ethinyl estradiol | 0.030 mg | |
| Red pills | Placebo/reminder pills | |

| Ortho 777-21 | ||
|---|---|---|
| White pills | Norethisterone | 0.500 mg |
| Ethinyl estradiol | 0.035 mg | |
| Light orange pills | Norethisterone | 0.750 mg |
| Ethinyl estradiol | 0.035 mg | |
| Orange pills | Norethisterone | 1.000 mg |
| Ethinyl estradiol | 0.035 mg | |

| Synphase T28 | ||
|---|---|---|
| Pale blue pills | Norethisterone | 0.5 mg |
| Ethinyl estradiol | 0.035 mg | |
| White pills | Norethisterone | 1.0 mg |
| Ethinyl estradiol | 0.035 mg | |
| Orange pills | Placebo/reminder pills | |

| Triquilar 21 | ||
|---|---|---|
| Reddish brown pills | Levonorgestrel | 0.050 mg |
| Ethinyl estradiol | 0.030 mg | |
| White pills | Levonorgestrel | 0.075 mg |
| Ethinyl estradiol | 0.040 mg | |
| Yellowish brown pills | Levonorgestrel | 0.125 mg |
| Ethinyl estradiol | 0.030 mg | |

| Triquilar 28 | ||
|---|---|---|
| Reddish brown pills | Levonorgestrel | 0.050 mg |
| Ethinyl estradiol | 0.030 mg | |
| White pills | Levonorgestrel | 0.075 mg |
| Ethinyl estradiol | 0.040 mg | |
| Yellowish brown pills | Levonorgestrel | 0.125 mg |
| Ethinyl estradiol | 0.030 mg | |
| Red pills | Placebo/reminder pills | |
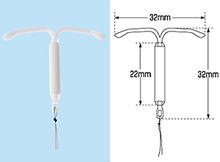
IUDs
IUDs, or Intra-Uterine Devices, are long term birth control devices that can be used for years before needing to be replaced. To learn more about how IUDs are inserted, how they work, and their effectiveness, visit Planned Parenthood for reliable information at: https://www.plannedparenthood.org/learn/birth-control/iud
Non-copper/Non-hormonal
Copper
Multiload

Hormonal
| Japanese | Romaji | English |
|---|---|---|
| セックス | sekkusu | sex/ sexual intercourse |
| 避妊具 (ひにんぐ) |
hiningu | contraceptives |
| 経口避妊薬 (けいこうひにんやく) |
keikouhininyaku | oral contraceptives |
| 子宮内避妊器具 (しきゅうないひにんきぐ) |
shikyuunaihininkigu | IUD (Intrauterine Device) |
| 緊急避妊ピル (きんきゅうひにんぴる) |
kinkyuuhininpiru | Morning-After Pill |
| 膣 (ちつ) |
chitsu | vagina |
| 子宮 (しきゅう) |
shikyuu | uterus |
| 子宮頸部 (しきゅうけいぶ) |
Shikyuukeibu | cervix |
| 卵管 (らんかん) |
rankan | Fallopian tubes |
| 卵巣 (らんそう) |
ransou | ovaries |
| 排卵 (はいらん) |
hairan | ovulation |
| 卵子 (らんし) |
ranshi | egg/ovum |
| 生理 (せいり) |
seiri | period/menstrual cycle |
| 生理痛 (せいりつう) |
seiritsuu | menstrual pain/cramps |
| 出血 (しゅっけつ) |
shukketu | bleeding/menstrual flow |
| 子宮内膜症 (しきゅうないまくしょう) |
shikyuunaimakushou | endometriosis |
| 子宮筋腫 (しきゅうきんしゅ) |
shikyuukinshu | uterine fibroids |
| 子宮内膜ポリープ (しきゅうないまくぽりーぷ) |
shikyuunaimakuporiipu | uterine polyps |
| 多嚢胞性卵巣症候群 (たのうほうせいらんそうしょうこうぐん) |
tanouhouseiransoushoukougun | Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) |
| 月経困難症 (げっけいこんなんしょう) |
gekkeikonnanshou | dysmenorrhea |
| 月経過多 (げっけいかた) |
gekkeikata | menorrhagia |
More in Medical & Health
Personal Care Daily Life